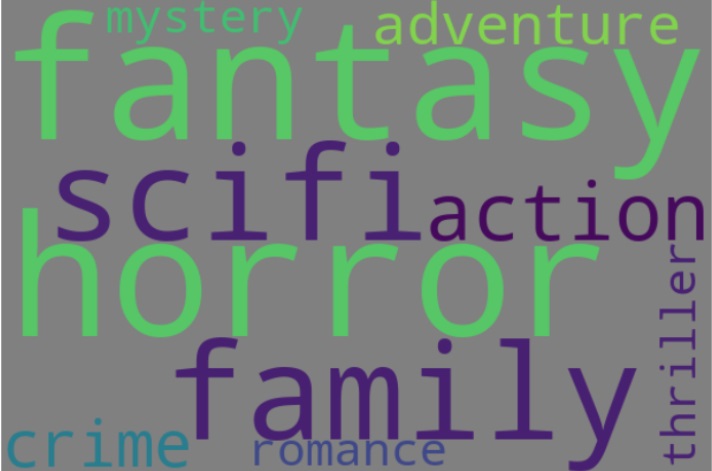|
Hi, I am Mehdi
Welcome to my personal webpage! As a Principal Data Scientist, my expertise encompasses diverse areas such as Advanced Machine Learning, Predictive Modeling, Customer Analytics, and Segmentation. I specialize in developing and deploying cutting-edge Large Language Models (LLMs) and Generative AI solutions. Holding a PhD in Geostatistics from the University of Alberta, I bring extensive experience across various industries, including finance (banking), telecommunications, engineering (oil & gas), and academia. I have shared some of my notable projects, blogs, lectures, and publications. Feel free to reach out if you have any questions or would like to connect! |
Selected Projects
Over the years as a data scientist, I have encountered and addressed a variety of real-world data science challenges. Below, you’ll find a curated selection of projects that demonstrate my approach to solving these problems. Each project includes both code and documentation to provide a clear understanding of the issue and its solution. Links to Python code, notebooks, and the public datasets used are provided, enabling you to explore and run the notebooks on your own.
|
Multi-RAG Workflow with LangGraph
READ MORE
Multi-source RAG pipeline built with LangGraph, orchestrating retrieval, grading, query refinement, and answer generation in a structured workflow. Documents are fetched from multiple sources, chunked, and evaluated using an LLM-based relevance grader. When retrieval quality is low, queries are automatically rewritten, with a web-search fallback to ensure missing information is covered. LangGraph coordinates multi-step reasoning and supports processing and summarizing multiple questions. The pipeline generates clean, synthesized outputs and performs a final quality evaluation. Results are compiled into a report and automatically emailed on a schedule, with full automation supported via GitHub Actions. |
|
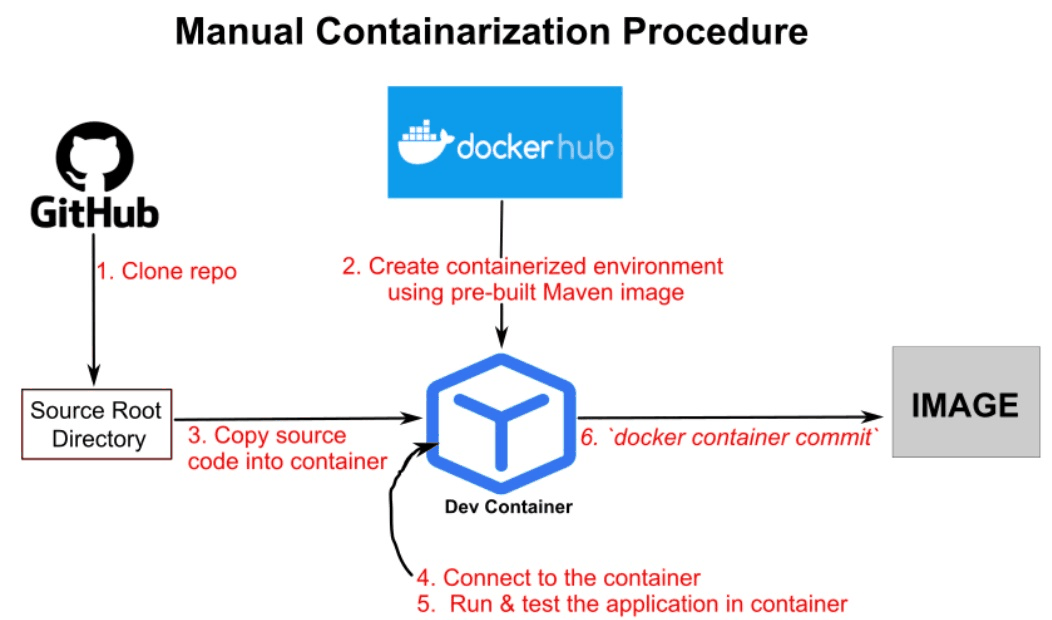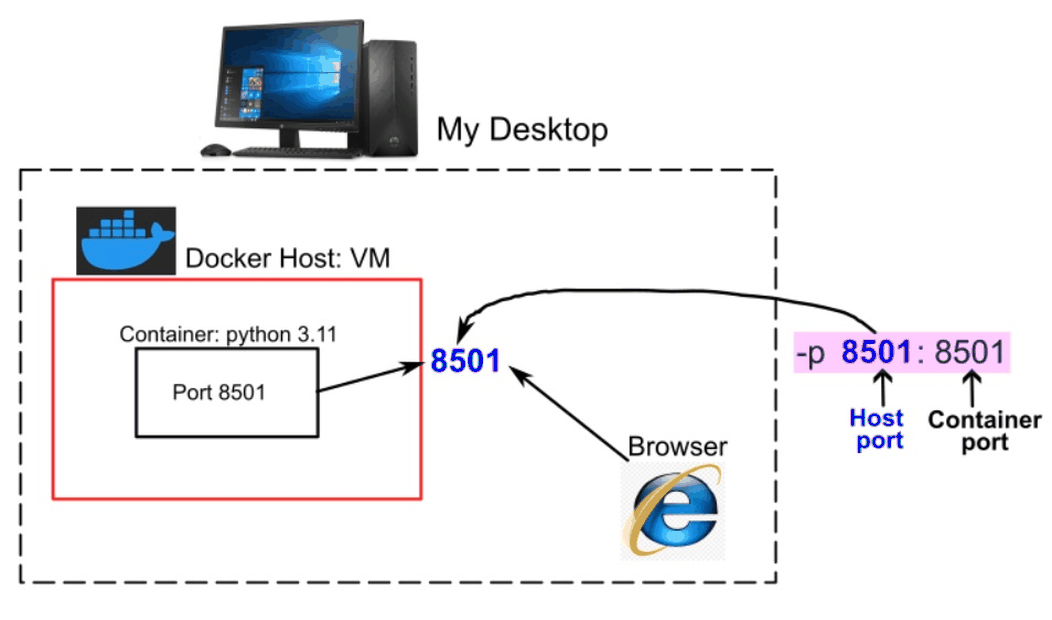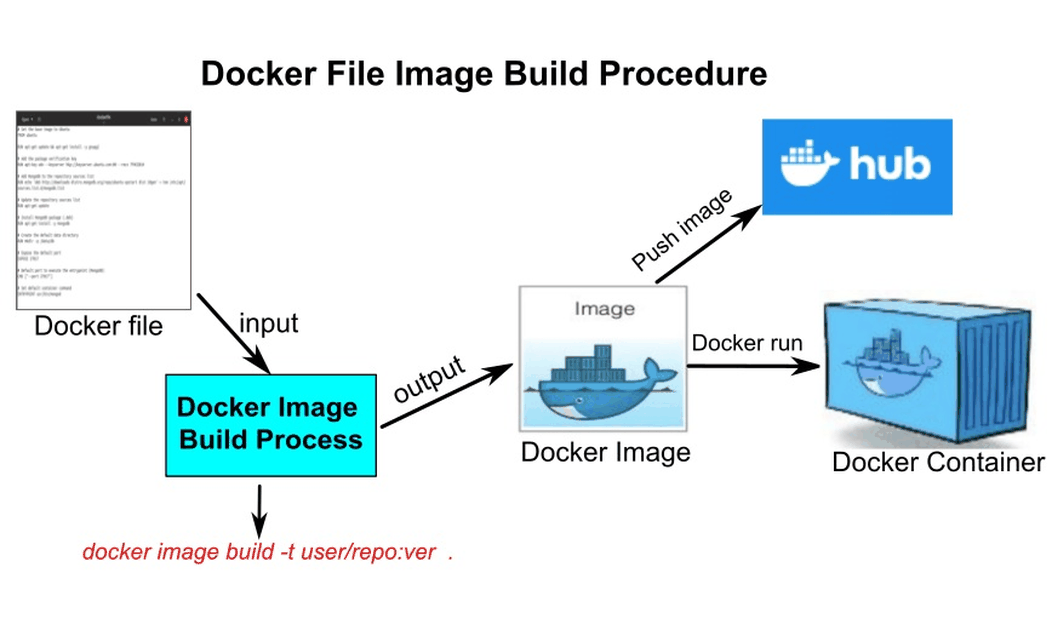
Containerizing Machine Learning Model with Docker
READ MORE
Demonstrating an end-to-end containerization workflow for a machine learning application, from model training to production deployment. It covers training a model, saving artifacts, and packaging the app using both manual Docker image creation and a Dockerfile-based approach. The process includes building, tagging, and pushing images to Docker Hub, followed by deployment on Hugging Face Spaces (free tier) as a fully hosted web application. |
|
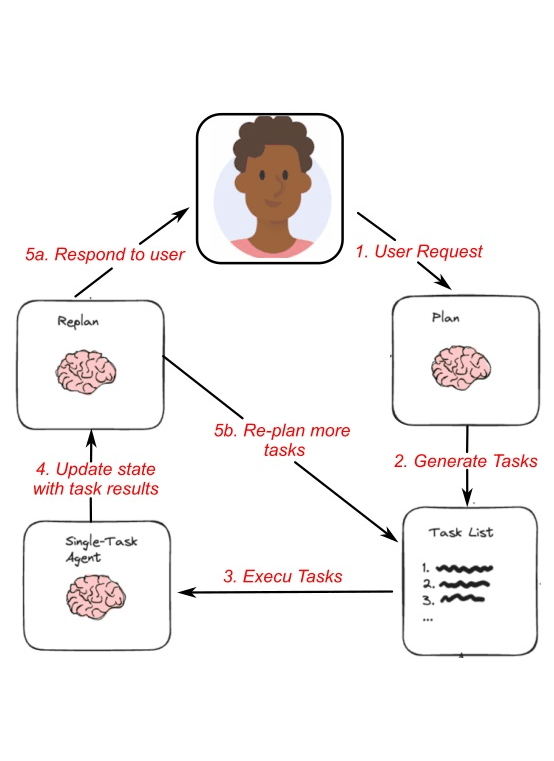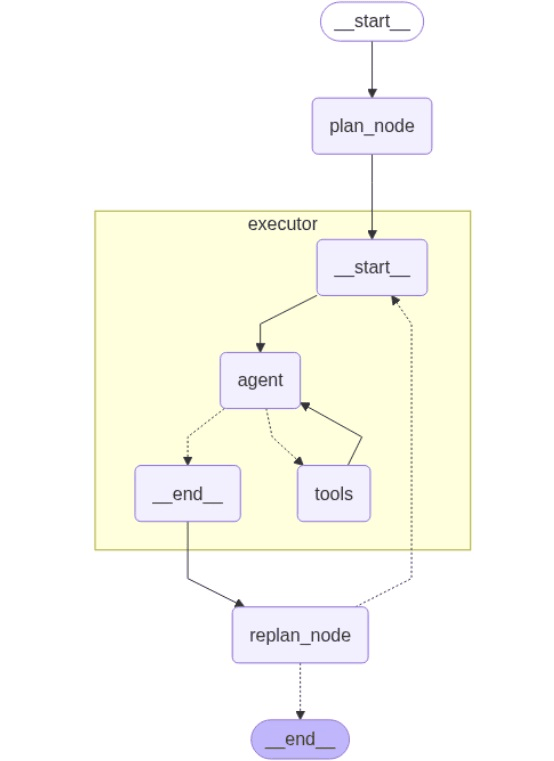
Planning & Execution Agents with LangGraph
READ MORE
A multi-step agent workflow built with LangChain and LangGraph is used to solve complex tasks through structured planning and execution. User queries are decomposed into smaller steps that are executed sequentially, with dynamic re-planning applied when needed. A dedicated planning state tracks inputs, intermediate actions, and final outputs throughout the process. External tools such as web search are integrated to support information retrieval and reasoning. The workflow is orchestrated using a graph-based architecture with distinct planning, execution, and re-planning nodes. This design enables robust multi-stage reasoning and accurate final responses. |
|
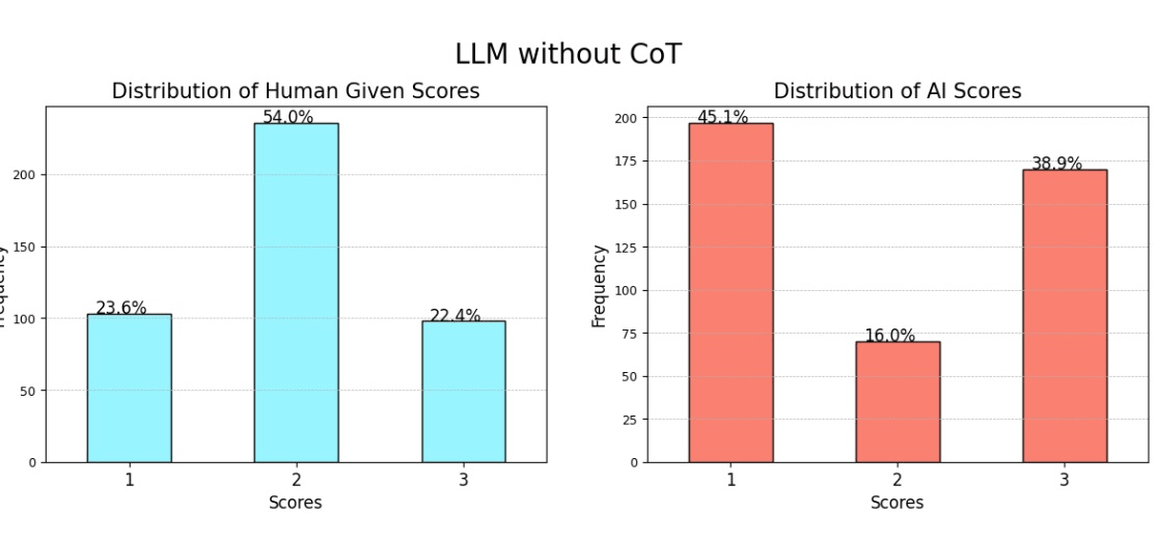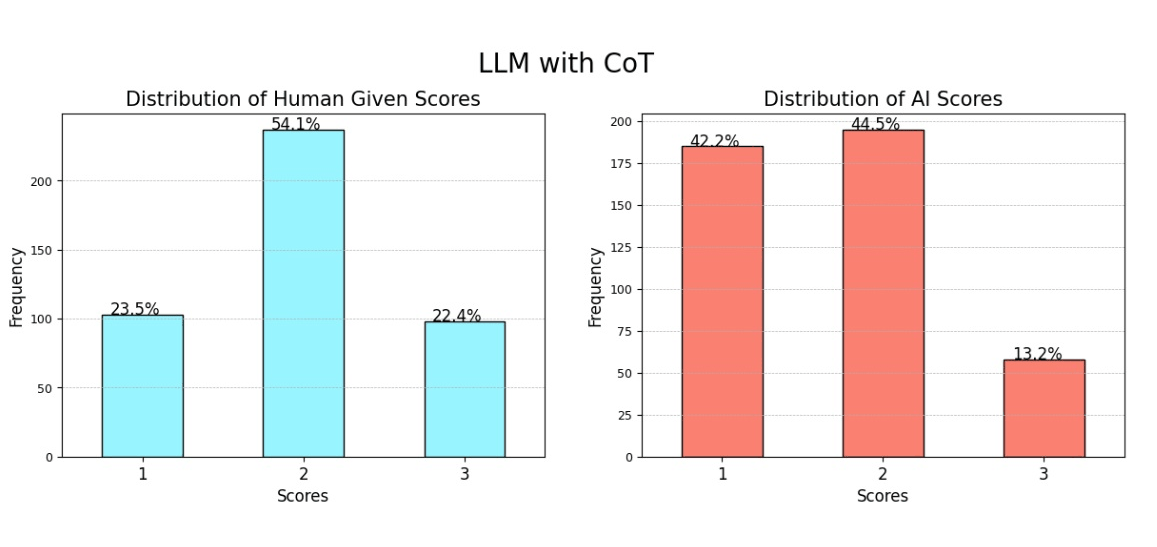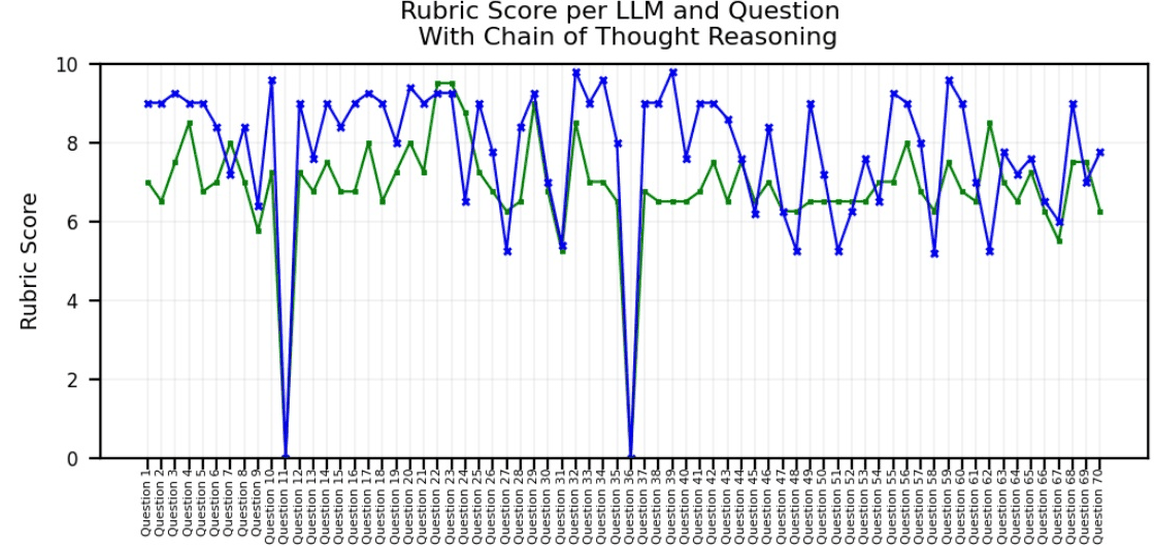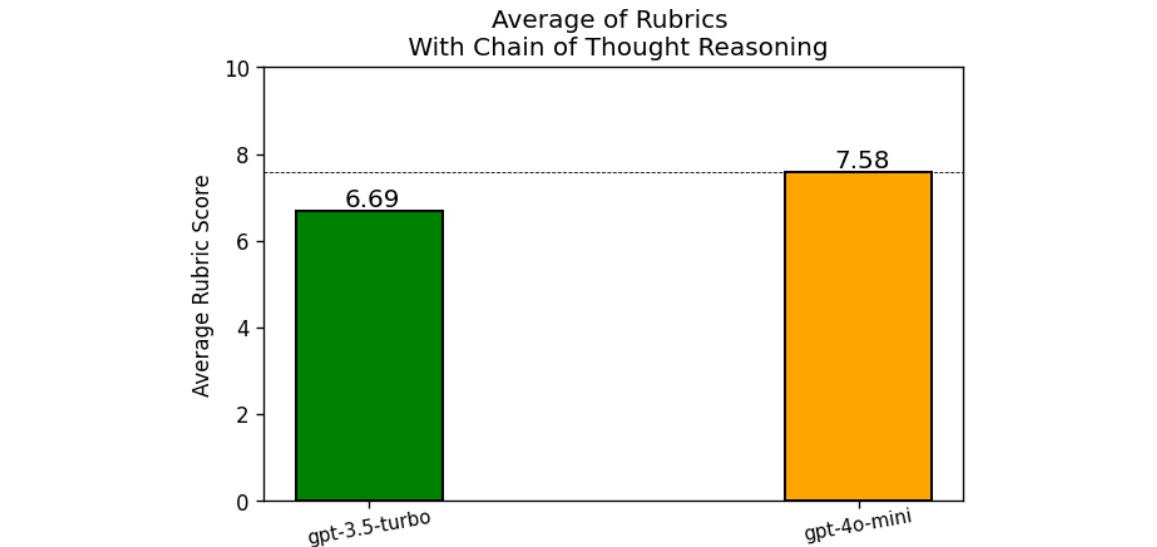
Evaluating LLMs: Metrics, Bias, and Reasoning Strategies
READ MORE
Introducing an evaluation framework for LLMs that highlights key metrics, rubric-based scoring, and positional bias. Demonstrating the impact of reasoning strategies like chain-of-thought and exploring methods to reduce bias in AI outputs. |
|
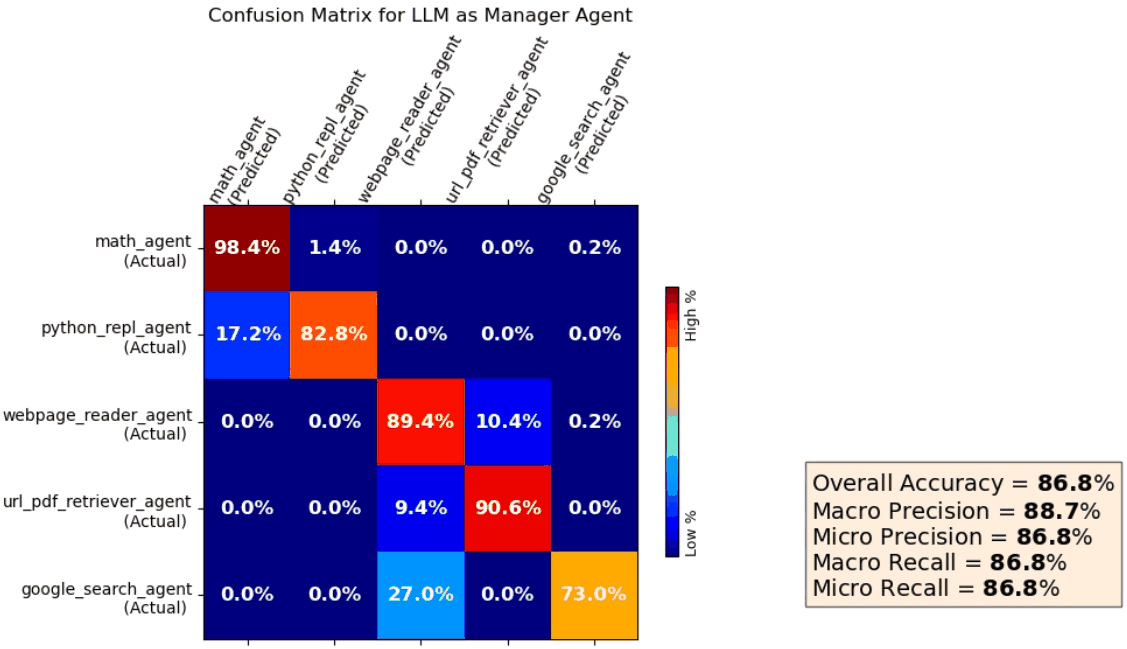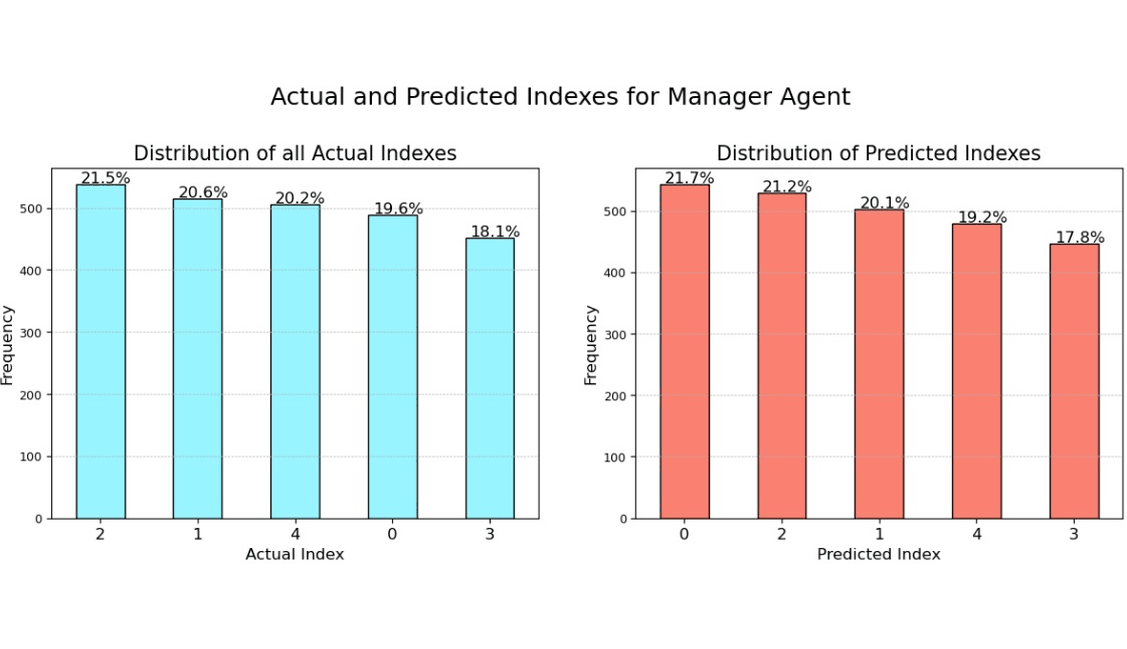
Evaluating LLM Tool Selection with LangChain Agents
READ MORE
Demonstrating AI agents built with LangChain and a structured framework for evaluating LLMs on tool selection tasks. A manager agent routes queries, captures intermediate reasoning, and applies rubric-based scoring to assess performance. The evaluation compares model behavior with and without chain-of-thought reasoning while analyzing positional bias. Practical examples highlight the impact of bias and strategies for mitigating it. |
|
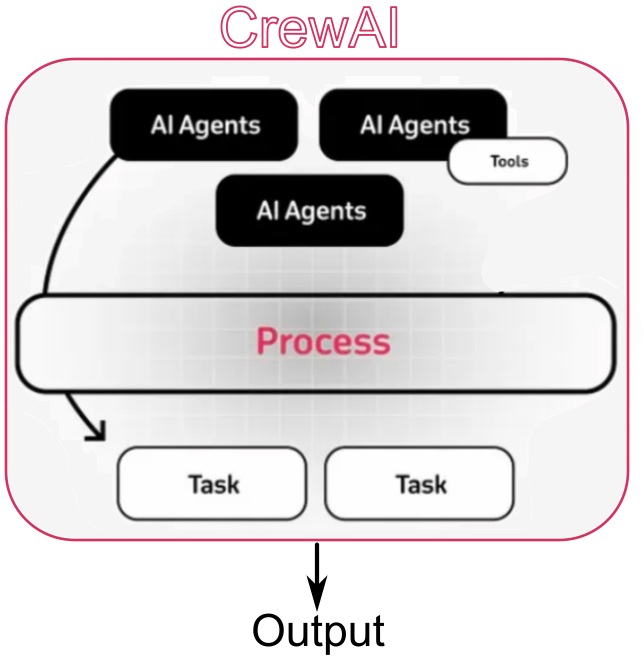
Multi-Agent Workflows with CrewAI and LangChain
READ MORE
Demonstrating collaborative, role-based AI agents built with CrewAI, designed to tackle complex tasks through teamwork and specialized roles. Each agent is assigned a specific function, enabling them to communicate, coordinate, and dynamically delegate subtasks for efficient problem-solving. The system supports both manager-driven and fully autonomous agent configurations, adapting to different workflows. External tools like LangChain and SerpAPI are integrated to retrieve real-time information from the web, enhancing decision-making. The gathered data is processed collaboratively to generate personalized, context-aware messages. This framework highlights the advantages of multi-agent collaboration over traditional single-agent approaches, emphasizing flexibility, scalability, and intelligent task sharing. |
|
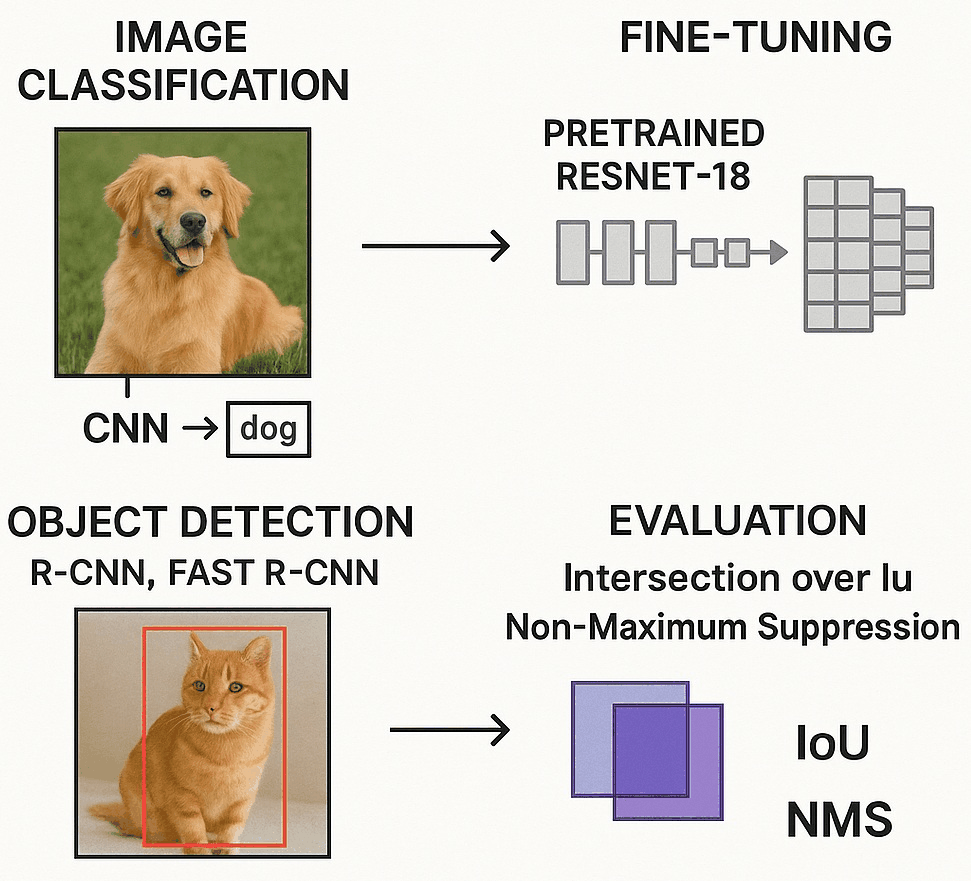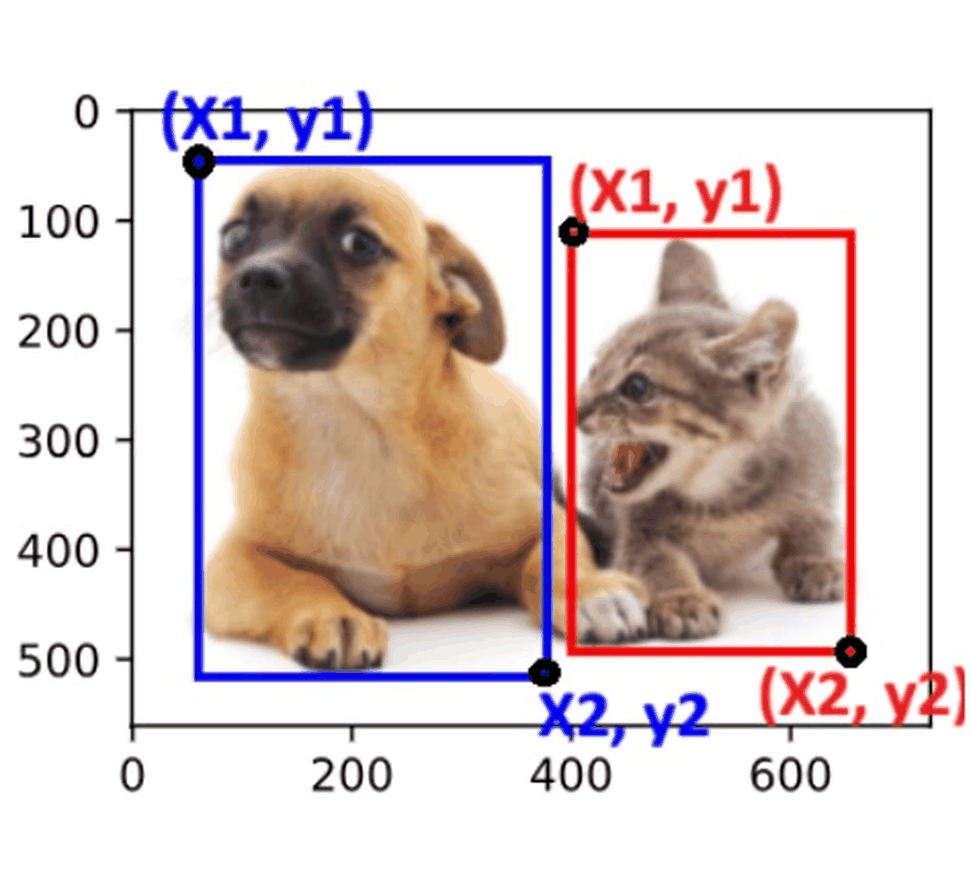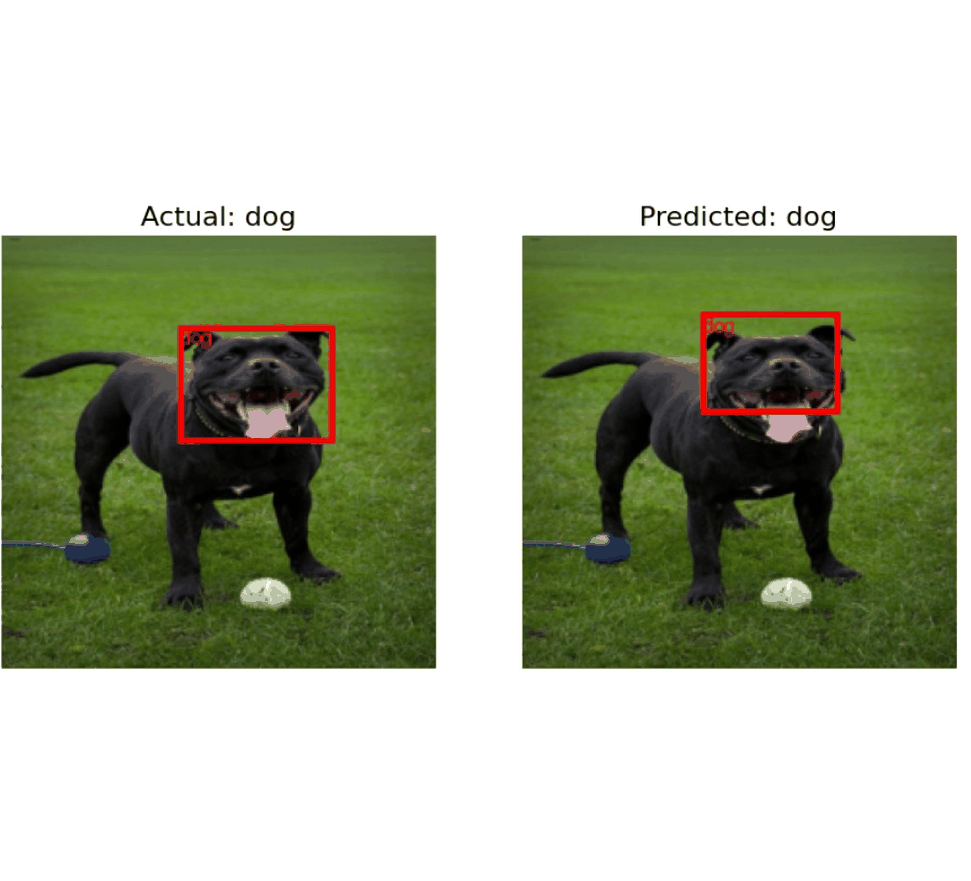
Deep Learning with PyTorch: From CNNs to Object Detection
READ MORE
Showcasing deep learning workflows in PyTorch, covering tasks from image classification to object detection. The workflow begins with building and training Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for image classification, followed by fine-tuning a pretrained ResNet-18 model to improve performance. It then introduces object detection using R-CNN and Fast R-CNN variants, demonstrating how to implement these models in PyTorch. Techniques for optimizing and evaluating model performance are highlighted, including Intersection over Union (IoU) and Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS). Practical examples illustrate both the training process and evaluation methods. |
|
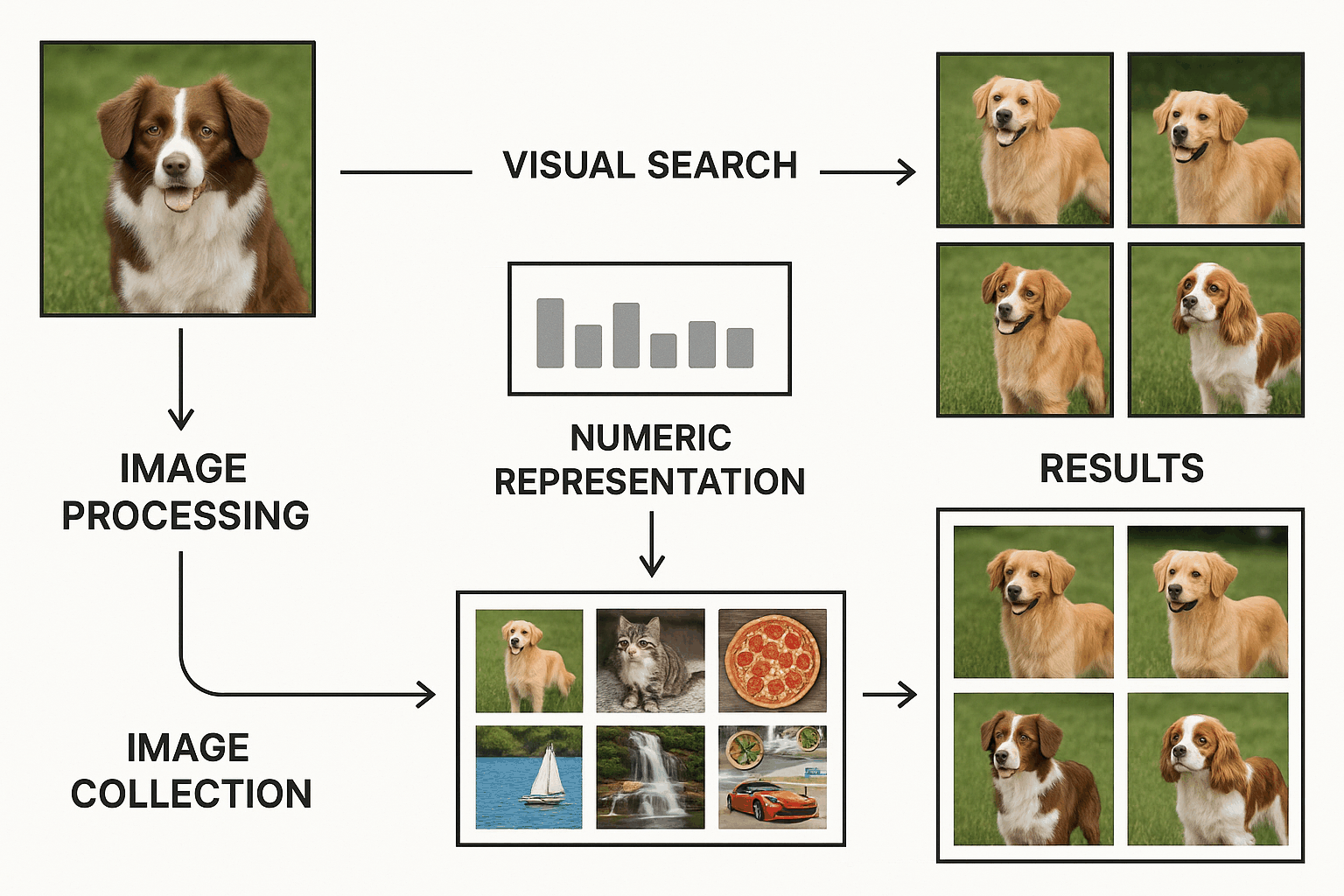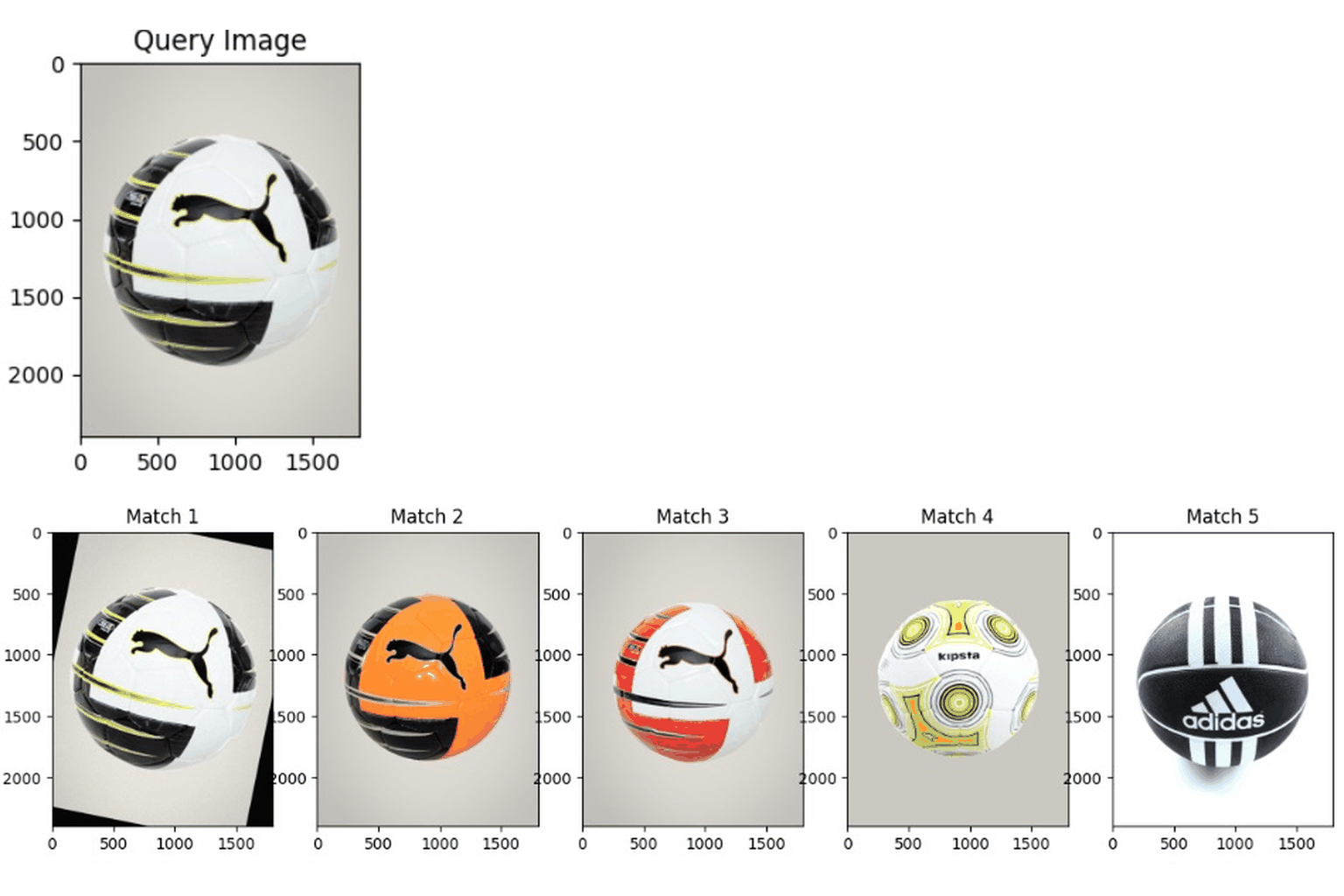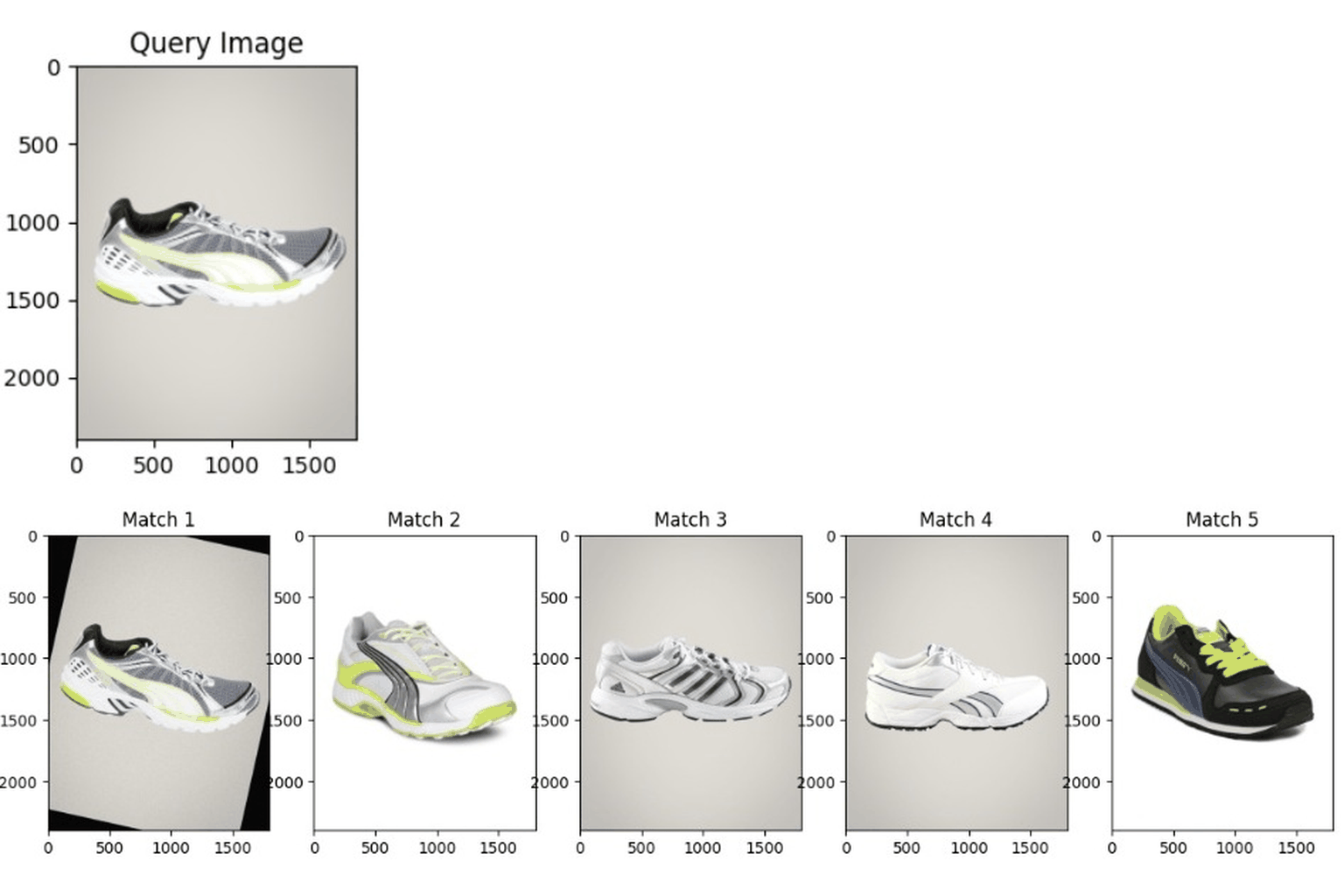
End-to-End Visual Search: Image Similarity Retrieval
READ MORE
Demonstrating a visual search system that uses image embeddings to find visually similar images. Images are converted into numeric representations capturing key visual features, which are then compared to retrieve matches. The system supports applications like duplicate detection, content recommendation, and organizing image collections. The workflow covers the full pipeline, from preprocessing and embedding generation to search and result visualization. |
|
LangChain in Action: LLM Applications with RAG and Agents
READ MORE
Demonstrating LangChain's capabilities through chat models, prompt templates, memory management, and chains. Highlighting advanced implementations like Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) and intelligent agents for Multi-Doc-Chatbots. Showcasing versatile, LLM-powered solutions. |
|
Fine Tune LLaMA-Model with Customer Support-Chatbot Dataset
READ MORE
Showcasing fine-tuning of the LLaMA model using a customer support chatbot dataset to improve response accuracy and domain-specific understanding. The model is optimized to handle industry-specific queries and provide context-aware responses. This enables practical applications such as customized conversational AI for businesses. The workflow highlights the importance of high-quality datasets in building robust and effective chatbots. |
|
Survival Analysis for Customer Churn
READ MORE
Applying survival analysis to Telco Customer Churn data to predict which customers are likely to leave. Both non-parametric and parametric methods, including Kaplan-Meier, Weibull, and Cox Hazard models, are used to analyze churn patterns. The approach accounts for censored data to provide more accurate timing predictions. Insights from the analysis reveal factors influencing churn and when it is most likely to occur. These findings can inform better business strategies for customer retention. |
|
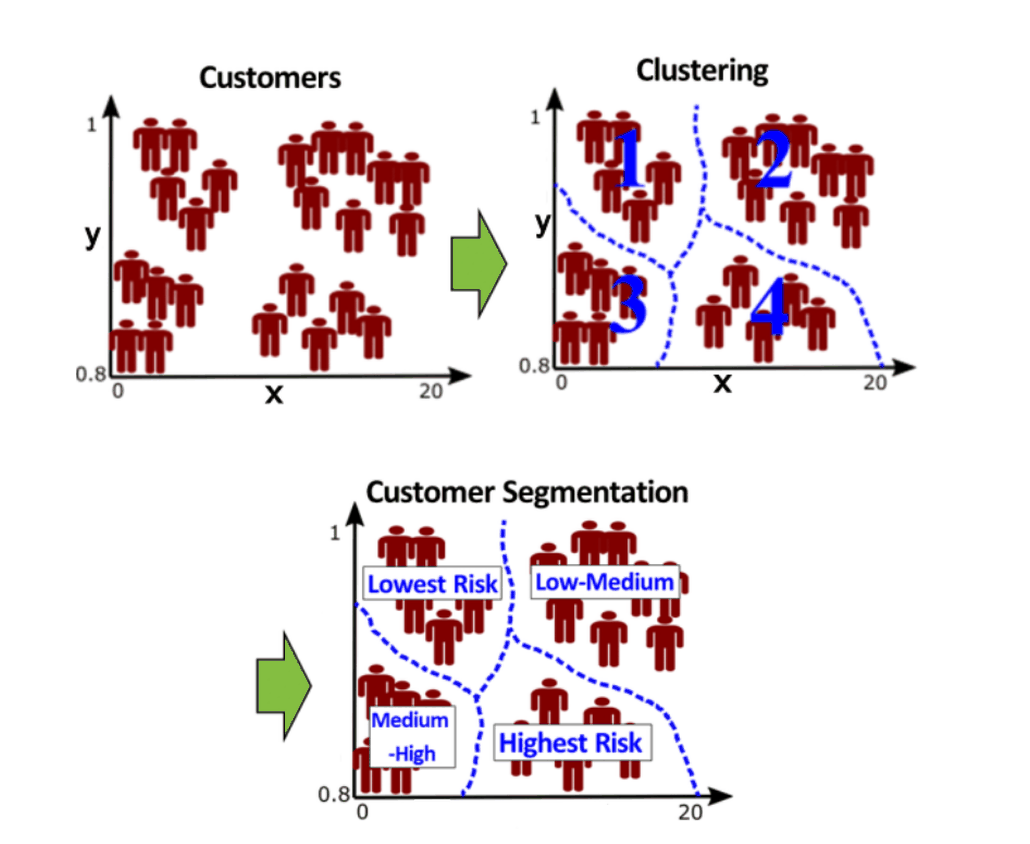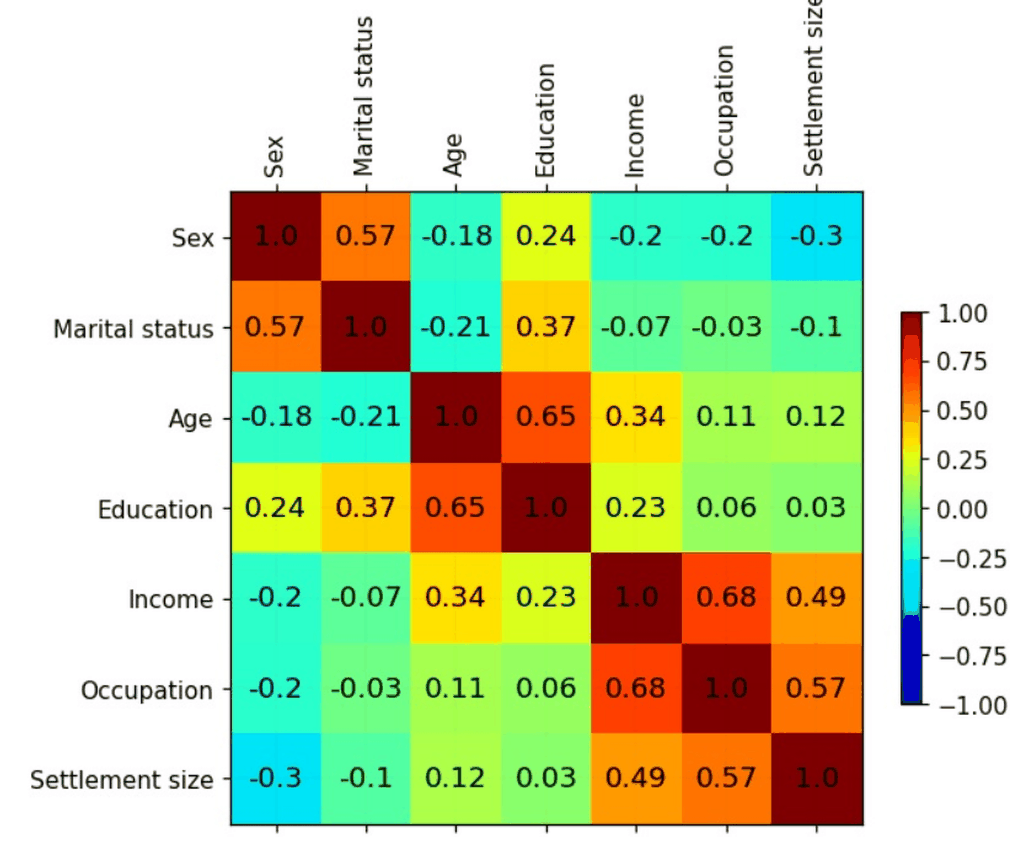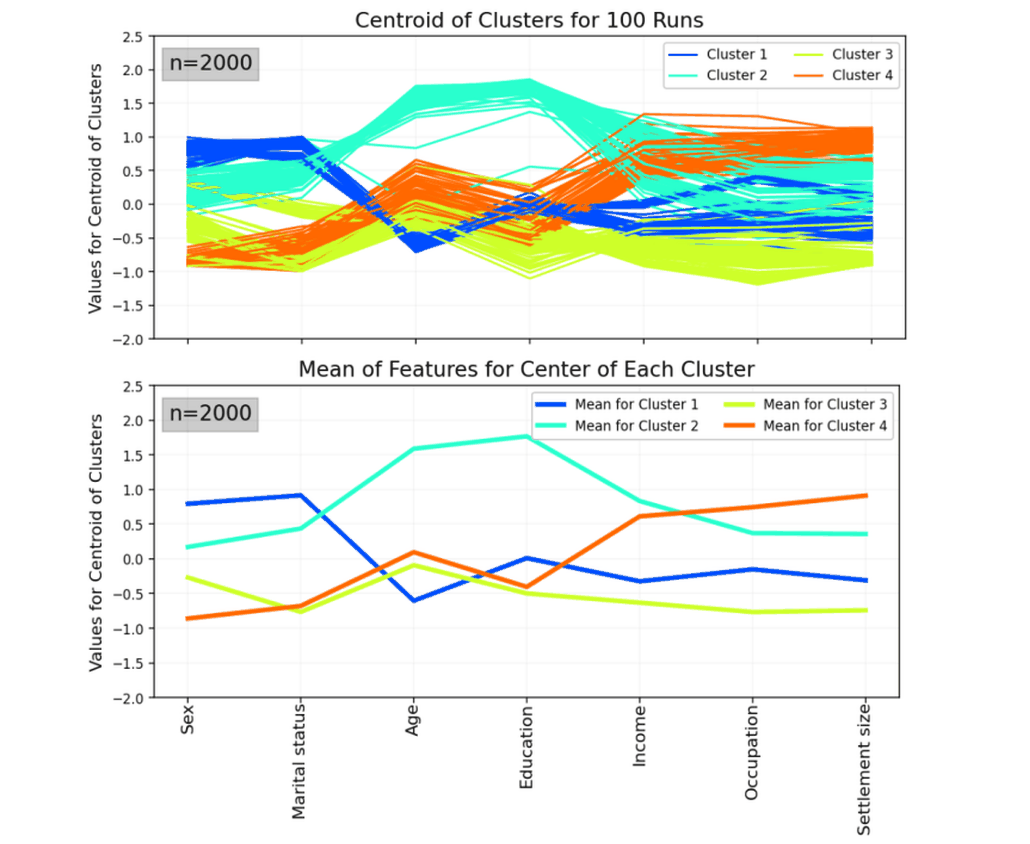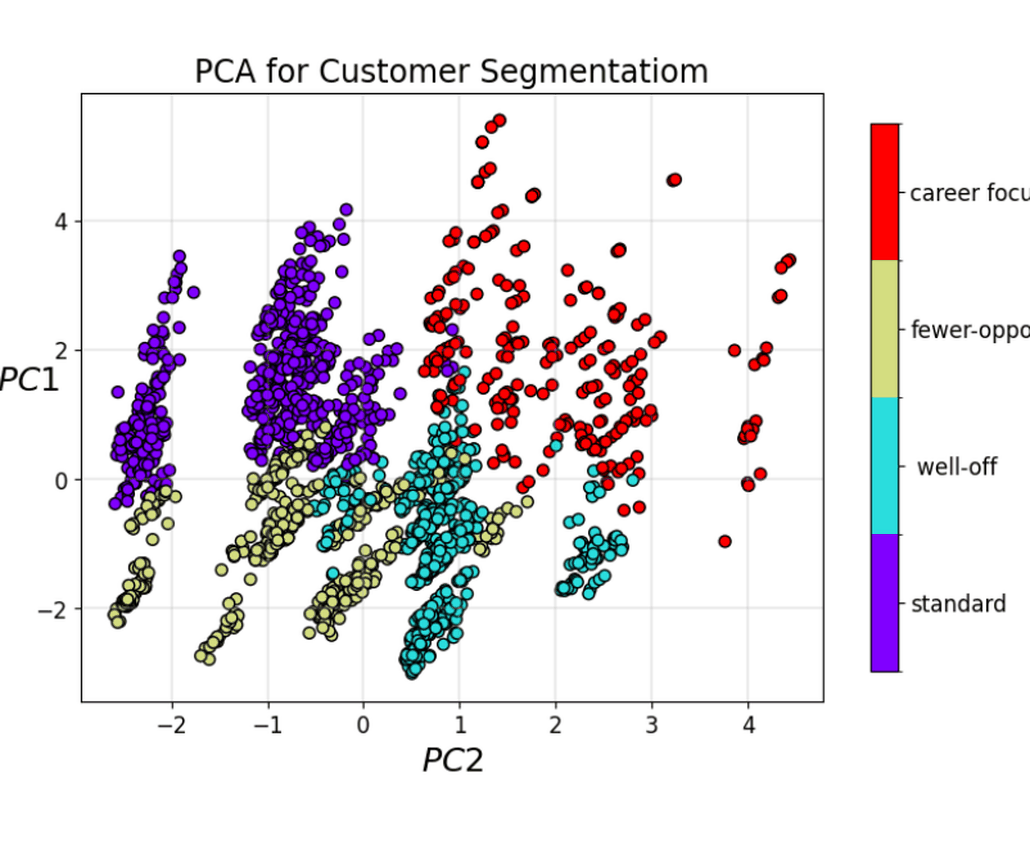
Customer Segmentation for Online Retail
READ MORE
Applying clustering to group customers based on behavior and interests, enabling more effective targeted marketing strategies. Mini-batch k-means is used to find optimal cluster centroids, repeated multiple times to ensure stability and avoid suboptimal solutions. Customer segments are defined by calculating the mean of features within each cluster, capturing distinct behavioral patterns. This segmentation allows marketers to tailor strategies for specific groups, such as promoting relevant offers or personalized campaigns. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is then applied to visualize the clusters and better understand relationships between customer groups. The workflow provides actionable insights into customer behavior and preferences. |
|
Streamlit App to Train Model for Customer Churn Prediction
READ MORE
Building a Streamlit app to train and deploy a customer churn prediction model with an interactive interface. Users can input data and view real-time churn risk predictions. The app includes tools for model training, evaluation, and insights into customer retention. Visualizations help interpret predictions and identify patterns. Hosted on Streamlit’s cloud, it provides an end-to-end workflow for actionable churn analysis. |
|
Classification With Imbalanced Class
READ MORE
Addressing imbalanced classification by applying resampling techniques (oversampling, undersampling, and combinations) to adjust class distribution in training data. Ensuring more balanced data for predictive models to improve minority class performance. Utilizing K-fold cross-validation to evaluate model accuracy, while noting challenges of overfitting due to class distribution differences. |
|
Time Series Prediction with Real-World Datasets
READ MORE
Applying time series prediction using realistic datasets, including Sunspots and Total Energy Consumption in Alberta. Both supervised learning methods—such as linear regression, neural networks, decision trees, and random forests—and deep learning models like RNN, LSTM, and GRU are used to forecast future values. The workflow emphasizes capturing temporal patterns and trends from historical data. Future predictions are accompanied by uncertainty estimates calculated through multiple simulations. This approach provides insights into expected future behavior and variability, aiding in more informed decision-making. |
|
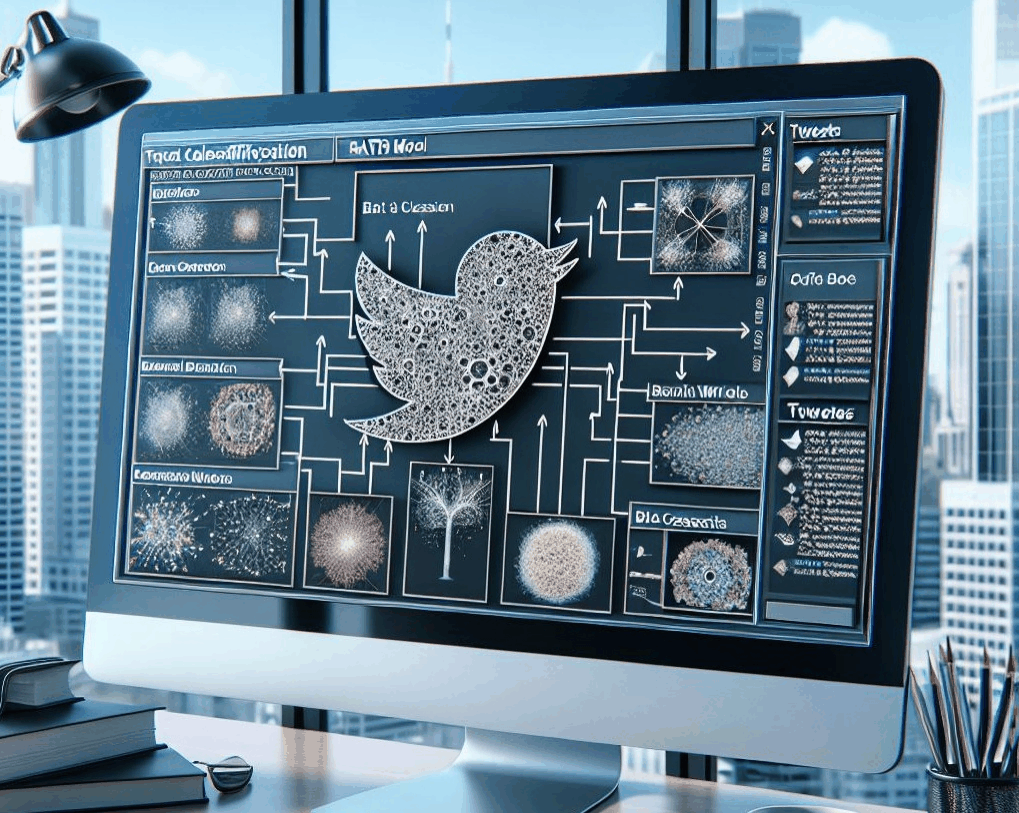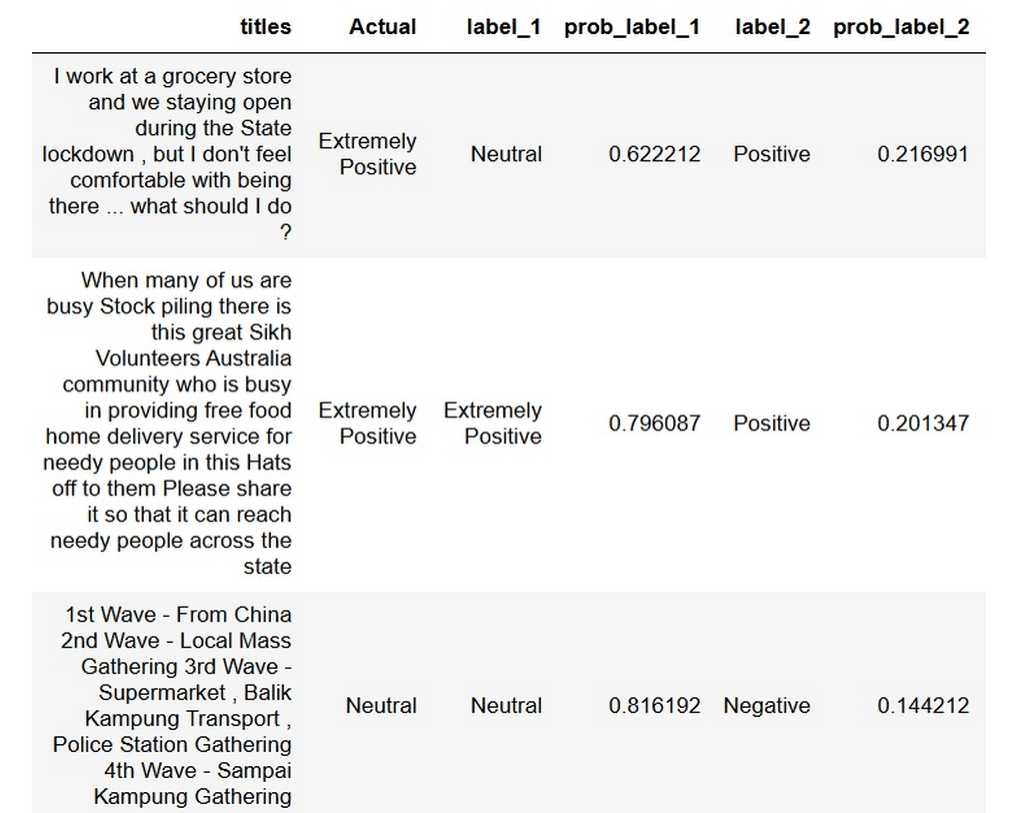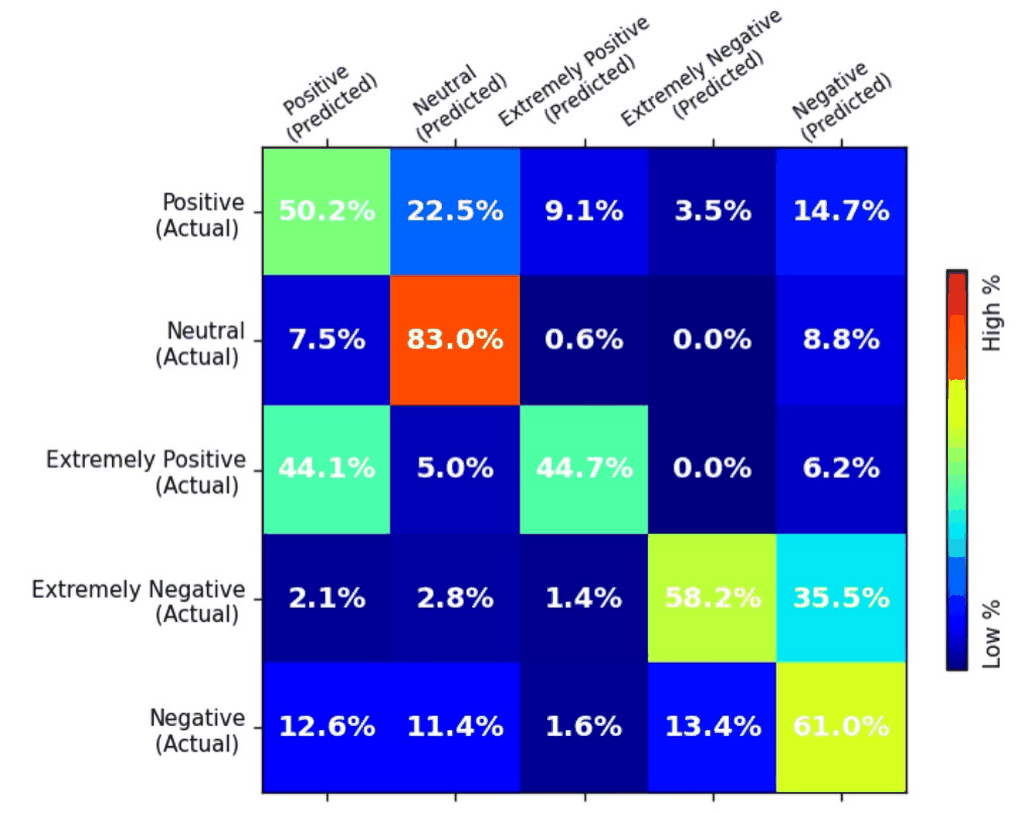
Fine-tune BART for Tweet Classification
READ MORE
Leveraging Facebook's BART model for sentiment classification on tweets. The workflow begins with zero-shot classification, allowing BART to predict tweet sentiments without task-specific training. A labeled dataset of tweets with five sentiment categories is then used to fine-tune the model. Fine-tuning adapts BART to the specific task, improving accuracy and precision in sentiment prediction. This approach demonstrates both the flexibility of pre-trained language models and the benefits of task-specific adaptation. The process provides reliable insights into public sentiment trends during the pandemic. |
|
Prediction of Serious Fluid Leakage for Alberta Well Energy
READ MORE
Using machine learning to predict serious fluid leakage in hydrocarbon wells in Alberta, Canada. Well properties such as age, depth, production history, and other operational factors are analyzed to assess leakage risk. Advanced imputation techniques and a range of predictive algorithms are applied to build reliable models. Class imbalance is addressed using oversampling and undersampling to improve prediction of the minority class. The study quantifies uncertainty and evaluates model performance with multiple metrics. This approach provides actionable insights for anticipating environmental risks and guiding preventive measures in hydrocarbon operations. |
|
Fine-Tuning BERT for Fake News Detection
READ MORE
Fine-tuning a pre-trained BERT model for fake news detection by adding a classification layer and training on a labeled dataset. Leveraging BERT's ability to capture contextual information for improved text classification. Exploring the process of adapting BERT for the specific task of detecting fake news. |
|
Majority Vote Technique for Feature Importance
READ MORE
Applying various predictive models, including Linear Regression, Decision Tree, Random Forest, and Gradient Boosting, to evaluate feature importance in regression and classification tasks. Techniques such as Coefficient of Determination and Predictive Power Score are used to quantify the relevance of input features. Multiple models are integrated using a majority vote approach to identify the most and least influential features. This workflow allows for a robust comparison of feature contributions across different algorithms. Both regression and classification problems are addressed to ensure general applicability. The approach provides clear insights into which features drive predictions and informs better model interpretation. |
|
Fine-Tuning GPT for Question Answering and Style Completion
READ MORE
Fine-tuning GPT-2 for tasks such as sentiment analysis, question answering, and text summarization using few-shot learning. The model is further adapted for “style completion,” enabling it to generate text in a specific writing style. Few-shot learning allows GPT-2 to perform new tasks with minimal task-specific examples. Fine-tuning adjusts the model’s parameters to improve accuracy and relevance for each task. This workflow demonstrates GPT-2’s versatility in handling diverse natural language processing applications. The study highlights its potential use in both research and industry settings for customized text generation and analysis. |
|
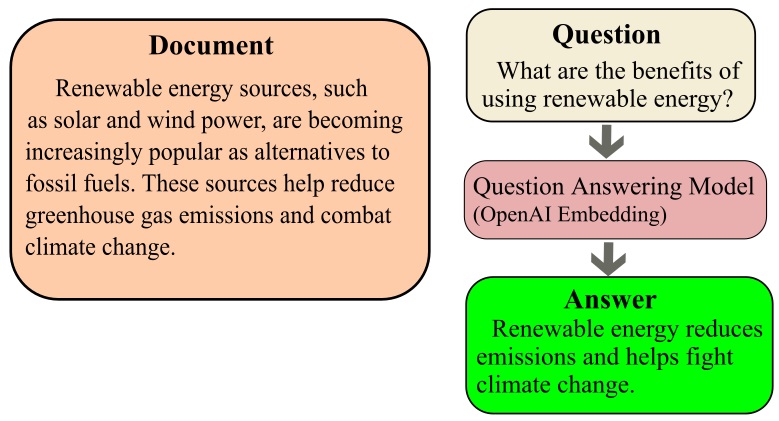
Abstractive Semantic Search by OpenAI
READ MORE
Using OpenAI embeddings for semantic search to improve accuracy by understanding query meaning rather than just keywords. The model generates embeddings for both queries and documents, ranking search results based on similarity. This approach enhances context-aware retrieval, as demonstrated by querying a book to find the most relevant answers. |
|
Fine-Tuning GPT for Movie Genre Prediction
READ MORE
Fine-tuning the distilgpt2 model (a more efficient version of GPT-2) for movie genre prediction. After pre-training on a large text corpus, the model is adjusted for the specific task of classifying movie genres based on plot summaries. This approach leverages the GPT architecture to enhance text classification, demonstrating its capability to predict movie genres with fine-tuned accuracy. |
Selected Blogs
The blogs featured below cover a wide array of topics in data science, machine learning, and related technologies. They range from practical tutorials, such as creating data science web apps with Streamlit, to in-depth discussions on advanced topics like statistical analysis, clustering, multicollinearity, and text similarity in NLP. Drawing from my hands-on experience, these posts aim to share knowledge and foster learning. Many include Python code, datasets, and notebooks for you to explore and replicate the analyses, while others focus on demystifying methodologies and tools. Dive in to gain practical insights and discover innovative solutions to data science challenges.
|
Exploring Containerization for Reproducible and Scalable ML Workflows
READ MORE
Demonstrating a practical guide to using Docker for ML and AI workflows, highlighting its role in ensuring reproducibility, portability, and scalability. It explains Docker vs. virtual machines, outlines benefits for ML engineers, data scientists, and DevOps, and shows how Docker fits across the entire ML lifecycle. Common use cases such as containerized notebooks, model serving, and cloud deployment are presented to illustrate how Docker enables consistent, efficient, and scalable ML systems. |
|
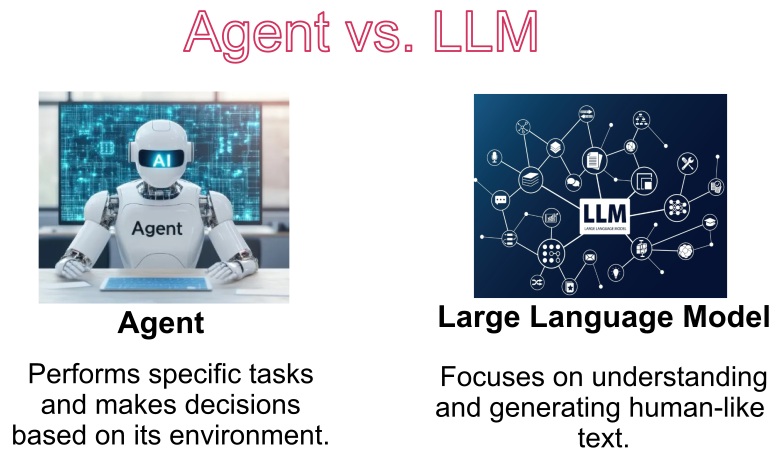
Comparing AI Agent Frameworks and Workflows
READ MORE
Exploring AI agents and comparing frameworks such as LangChain, CrewAI, and AutoGen for building modular, LLM-powered workflows. The discussion covers the structure, capabilities, and real-world applications of agentic systems. Differences between traditional agents and LLM-based agents are highlighted, including their strengths and limitations. Frameworks are evaluated based on design philosophy, flexibility, and suitability for various tasks. Practical examples illustrate how these tools can be used to create coordinated, multi-agent workflows. The comparison provides insights into designing intelligent and modular AI systems for diverse applications. |
|
Data Science Web App with Streamlit
READ MORE
Building interactive web apps with Streamlit for data visualization and machine learning model deployment. The platform enables quick development of user-friendly web interfaces to explore insights and predictions without extensive web development knowledge. Two customer churn prediction apps are featured: one using a pre-trained model for quick predictions, and another providing a full workflow to train a model from scratch. Streamlit’s integration with visualization libraries and interactive widgets allows real-time updates and dynamic exploration of data. These apps demonstrate practical applications of deploying machine learning models in an accessible, interactive format. The workflow highlights how Streamlit can streamline the process from data analysis to model deployment. |
|
Introduction to Hugging Face: Pre-trained Model and Tools
READ MORE
Exploring Hugging Face's contributions to natural language processing (NLP) through its open-source transformers library. Providing access to pre-trained models like BERT, GPT, and T5, ready to be fine-tuned for tasks like sentiment analysis, text classification, and summarization. Simplifying the fine-tuning process to enable researchers and developers to focus on specific applications without the complexity of model training. |
|
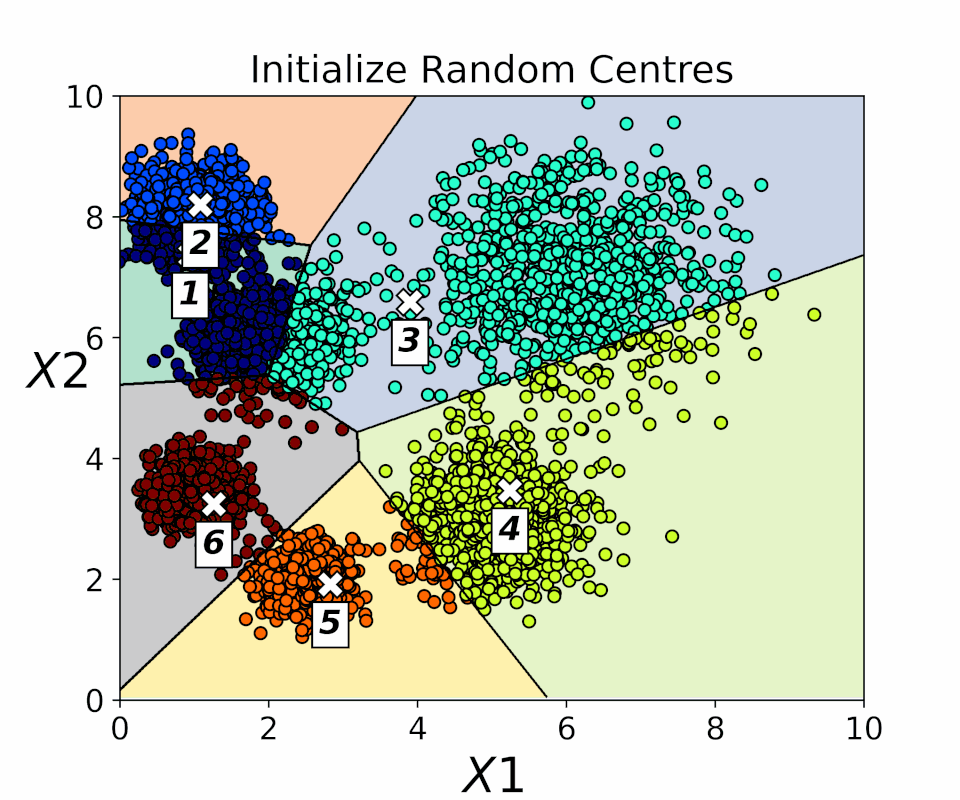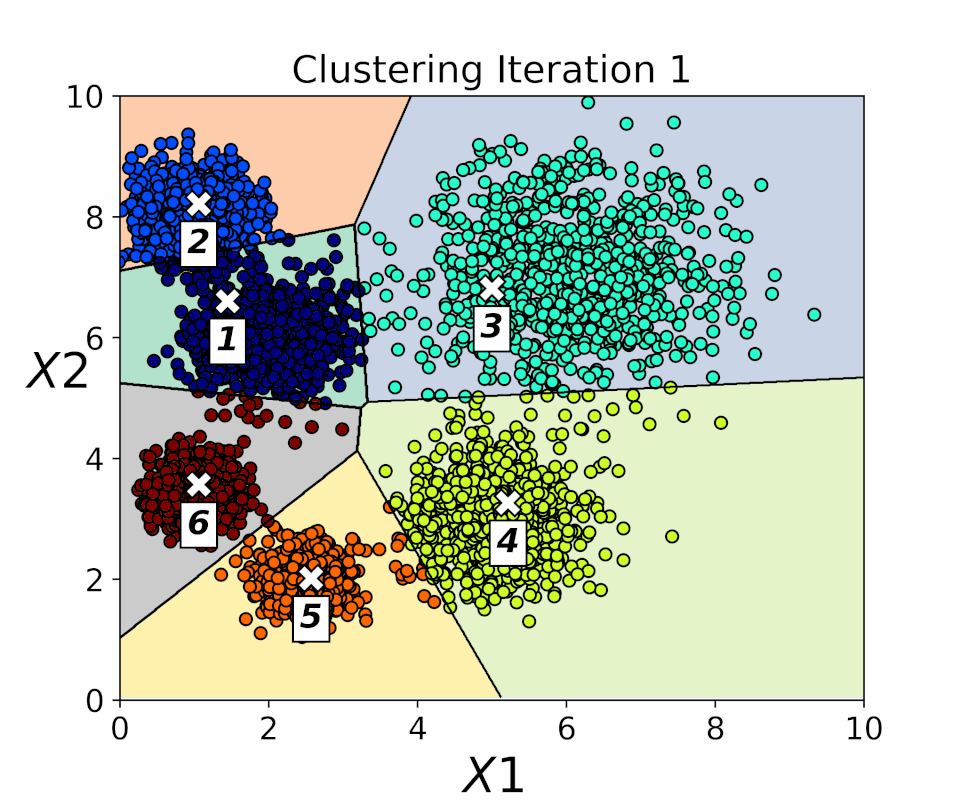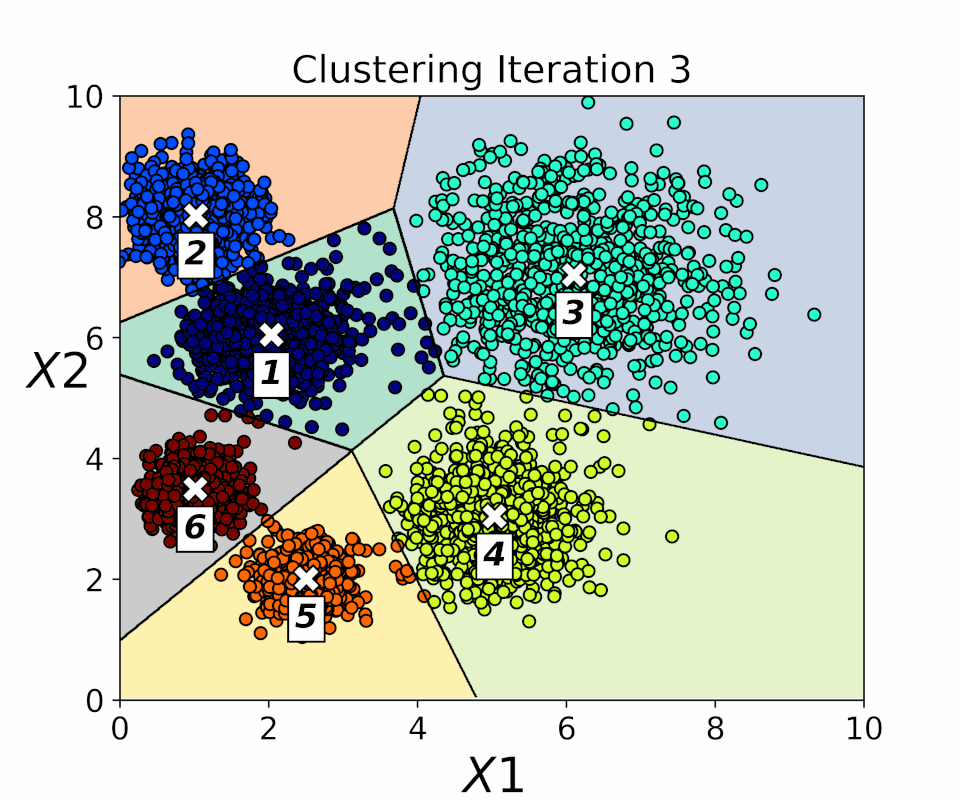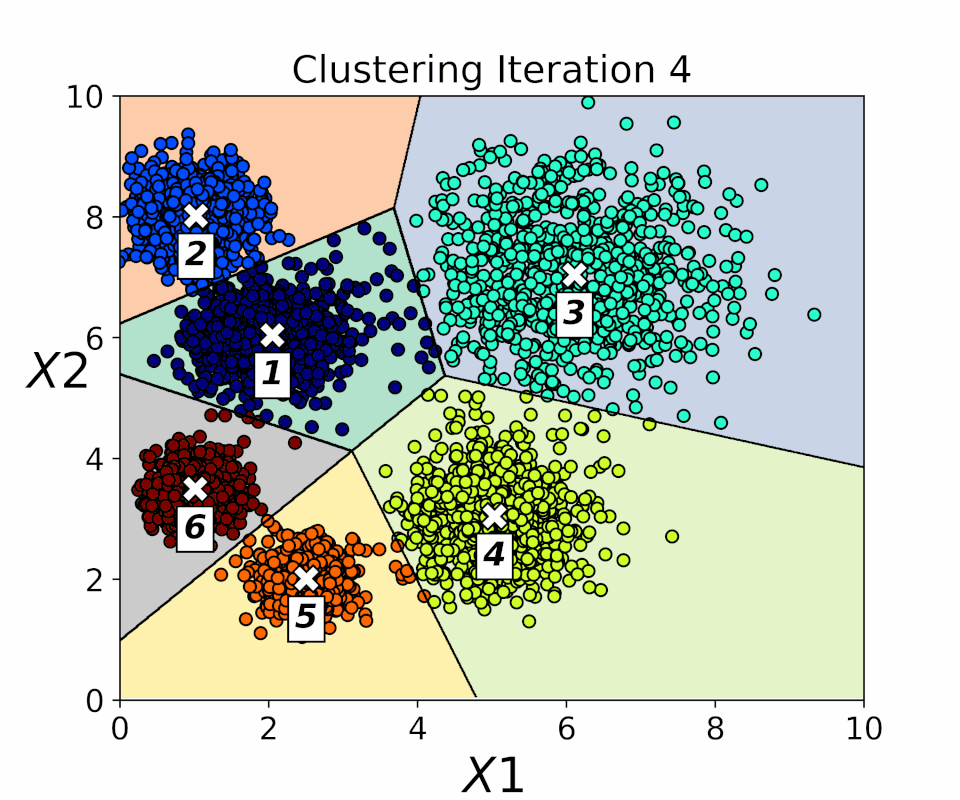
Exploring Clustering Techniques
READ MORE
Examining unsupervised machine learning techniques for grouping unlabeled data using clustering. Methods covered include K-means, DBSCAN, Spectral Clustering, Agglomerative Clustering, and Gaussian Mixture models, applied to both synthetic and real-world datasets. The workflow demonstrates how clustering can automatically identify patterns and group similar data points without human supervision. Advantages and limitations of each technique are discussed to guide effective data segmentation. This approach provides insights into selecting the most suitable clustering method for different types of data. Overall, it highlights the practical applications and challenges of unsupervised learning. |
|
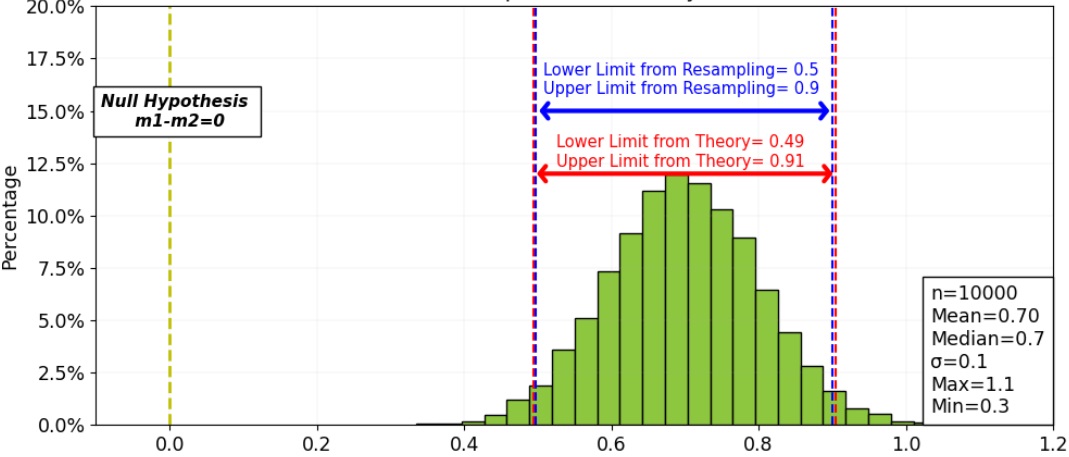
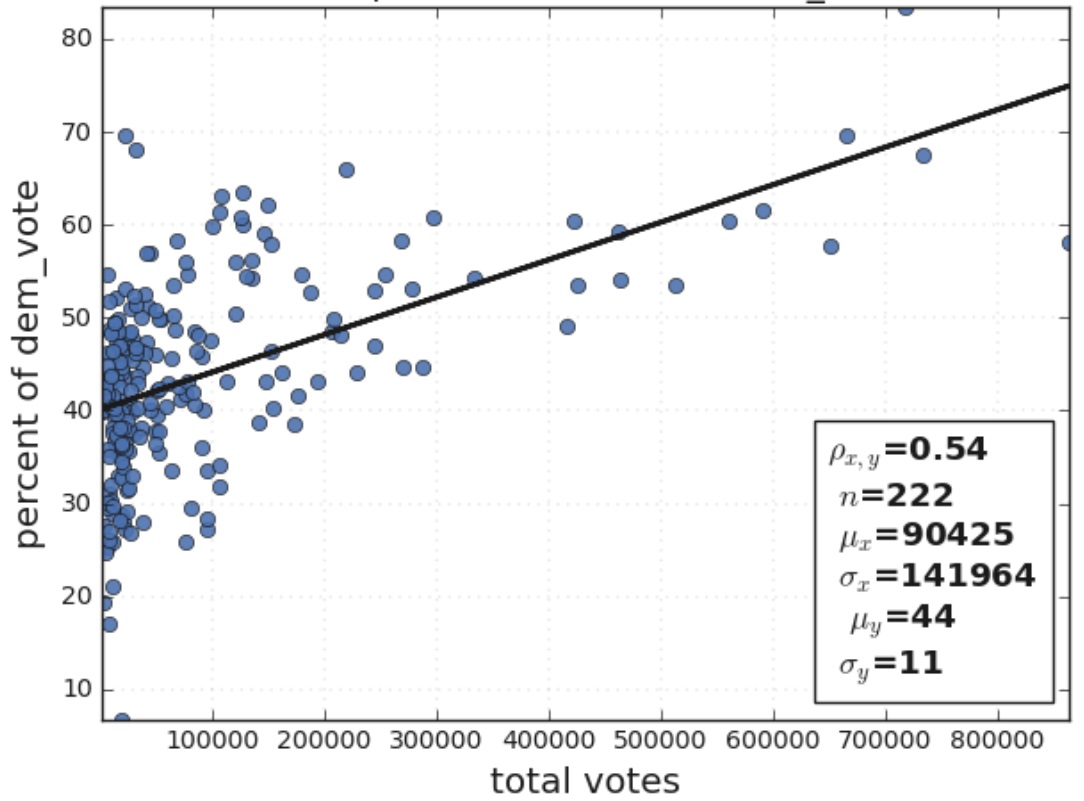
Statistical Analysis in Python
READ MORE
Implementing various statistical analysis techniques in Python, including bootstrapping, confidence intervals, hypothesis testing (z-test, t-test, f-test, chi-square), A/B testing, and effect size. Applying these methods to two real-world datasets: the 2008 US swing state election results and finch beak dimensions. |
|
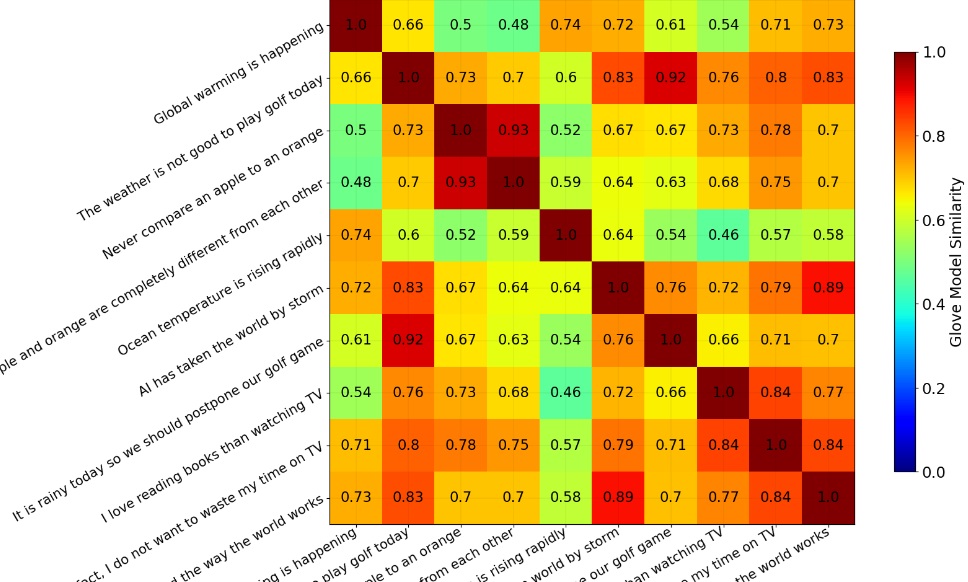
Text Similarity in NLP
READ MORE
Exploring text similarity techniques in natural language processing (NLP) to measure the closeness between two text chunks based on surface-level or meaning. Discussing methods like Jaccard similarity, Cosine similarity, Inverse Document Frequency, Glove pre-trained models, and Word Mover Distance. The focus is on both lexical (word-level) and semantic (phrase/paragraph-level) similarity, with an introduction to data processing for NLP. |
|
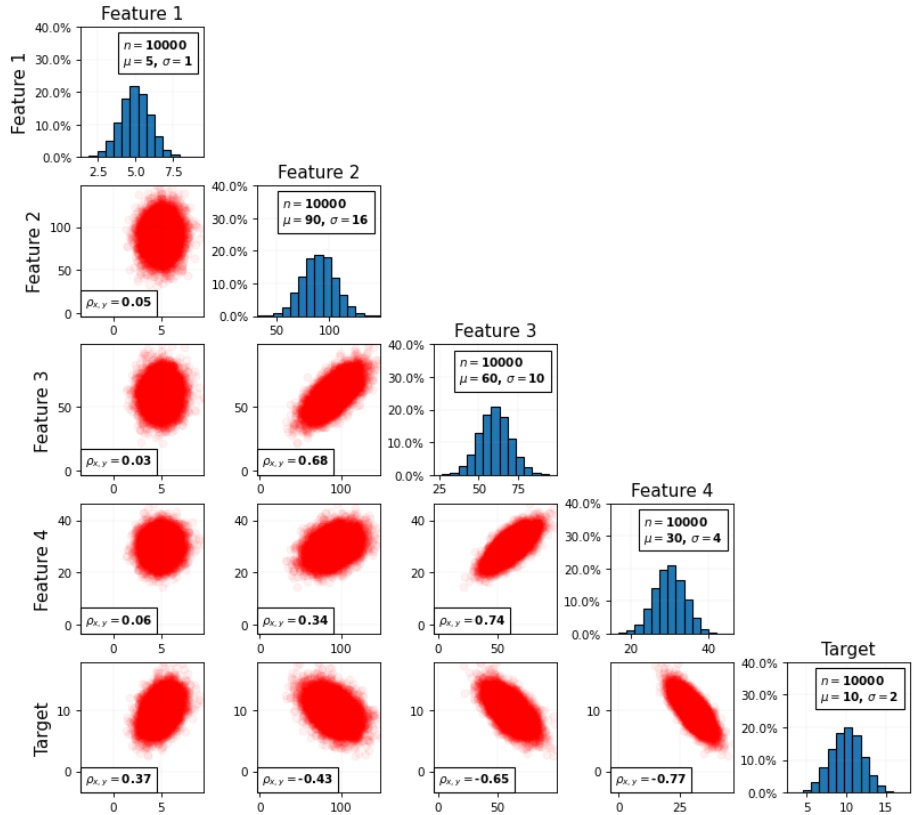
Detecting and Addressing Multicollinearity
READ MORE
Examining multicollinearity in multiple regression, where high correlation among independent variables affects the precision and interpretability of model coefficients. Methods such as p-values for regression coefficients and Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) are applied to detect multicollinearity. The workflow includes strategies to address and mitigate its impact on model reliability. Both synthetic and realistic examples are used to illustrate the detection and correction process. This analysis helps ensure that regression models produce accurate, interpretable results. |
|
Exploring LangChain for LLM-powered Applications
READ MORE
Exploring the use of LangChain to develop and deploy AI-driven applications using large language models (LLMs). LangChain simplifies the integration of LLMs with other systems for data retrieval and performance monitoring, addressing the complexities of working with diverse LLM architectures, training data, and use cases.. |
|
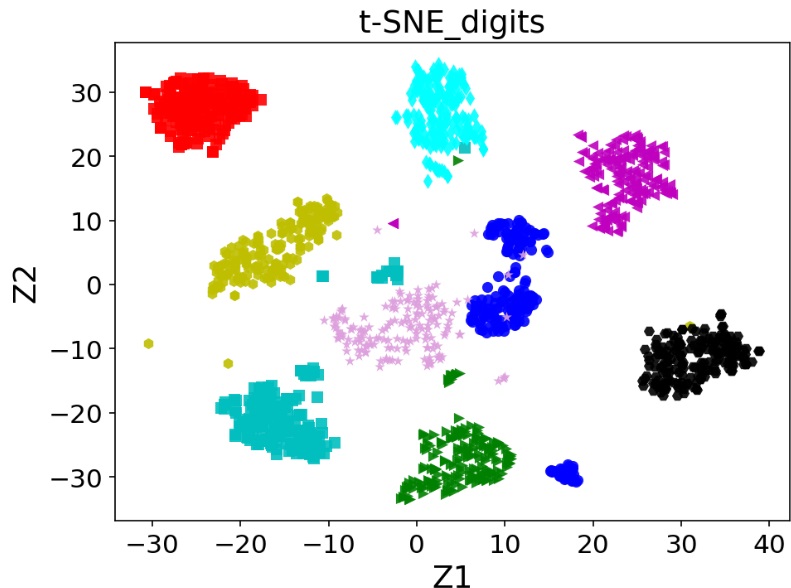
Dimensionality Reduction Techniques
READ MORE
Exploring unsupervised dimensionality reduction techniques to reduce the number of input variables while retaining key information. Methods such as PCA, t-SNE, LLE, and LDA are applied to manage high-dimensional data effectively. These techniques improve data visualization, reduce multicollinearity, and help mitigate overfitting. The workflow demonstrates projecting data into lower-dimensional subspaces that capture essential patterns. Implementation in Python illustrates how dimensionality reduction enhances model efficiency and reduces training time. Overall, the approach highlights practical strategies for handling complex, high-dimensional datasets. |
|
Exploratory Data Analysis and Statistical Visualization
READ MORE
Exploring different approaches for exploratory data analysis and statistical visualization, including histograms, CDF, swarm plots, box plots, and kernel density estimation. Discussing probability distributions like binomial, Poisson, normal, and exponential. Focusing on data manipulation and analysis using Pandas to uncover insights and trends in the data. |
|
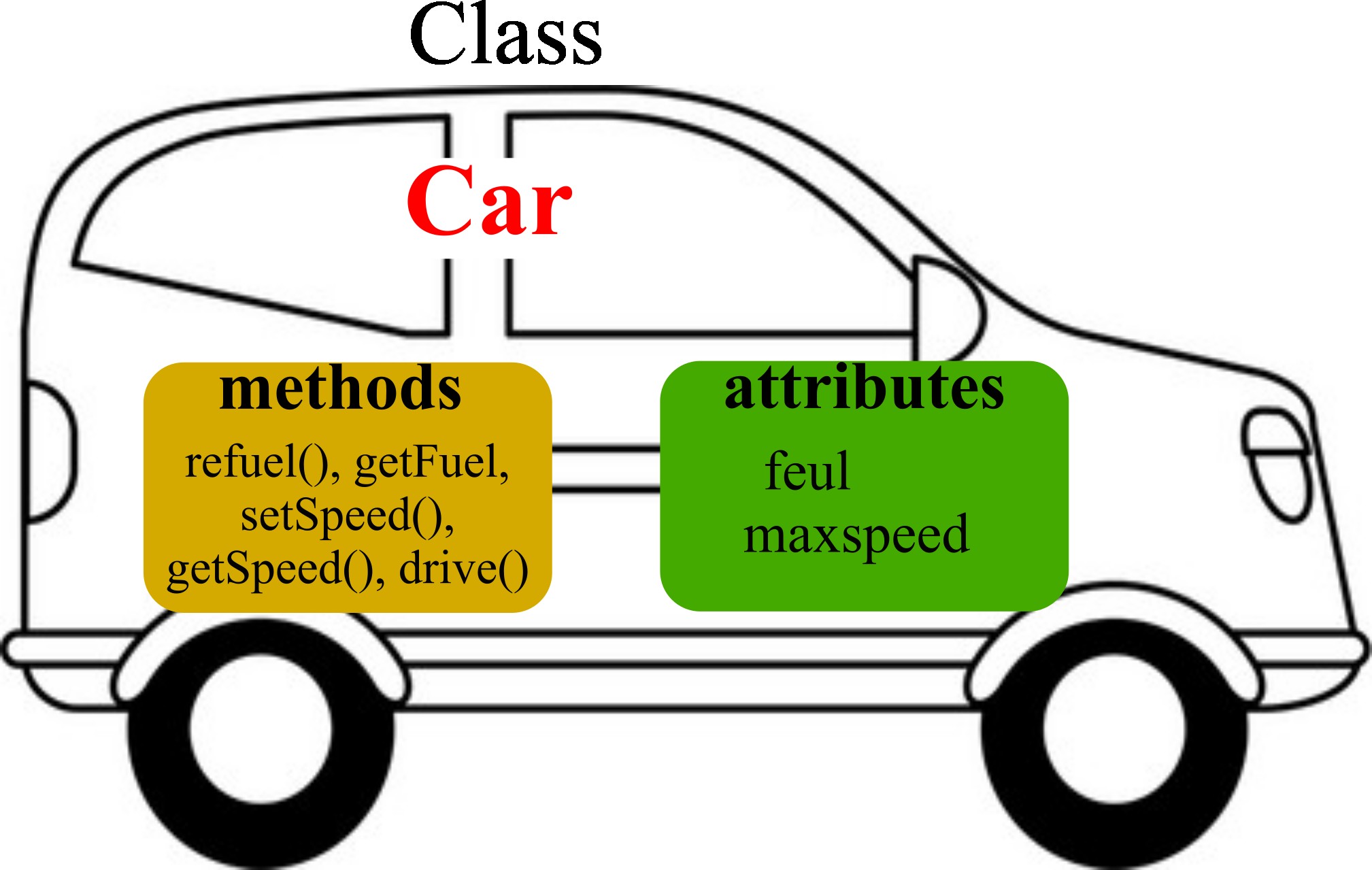
Object Oriented Programming in Python
READ MORE
Introducing Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in Python, focusing on the use of classes and methods. Highlighting key OOP concepts such as inheritance and polymorphism, which provide flexibility and enhance code reusability. |
Copyright 2025. All rights reserved!
Create a free web site with Weebly